Java String
In java, string is basically an object that represents sequence of char values. An array of characters works same as java string. For example:
char[] ch={'j','a','v','a','t','p','o','i','n','t'}; String s=new String(ch);
is same as:
String;
Java String class provides a lot of methods to perform operations on string such as compare(), concat(), equals(), split(), length(), replace(), compareTo(), intern(), substring() etc.
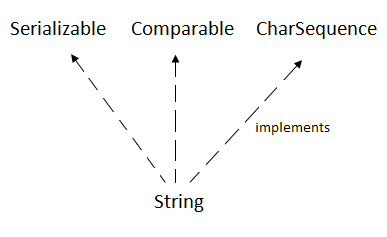
The java.lang.String class implements Serializable, Comparable and CharSequence interfaces.
 CharSequence Interface
CharSequence Interface
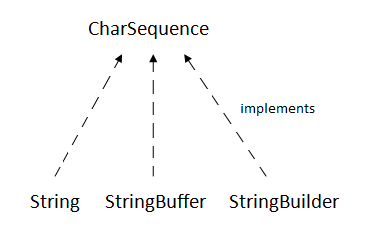
The CharSequence interface is used to represent sequence of characters. It is implemented by String, StringBuffer and StringBuilder classes. It means, we can create string in java by using these 3 classes.
The java String is immutable i.e. it cannot be changed. Whenever we change any string, a new instance is created. For mutable string, you can use StringBuffer and StringBuilder classes.
We will discuss about immutable string later. Let's first understand what is string in java and how to create the string object.
What is String in java
Generally, string is a sequence of characters. But in java, string is an object that represents a sequence of characters. The java.lang.String class is used to create string object.
How to create String object?There are two ways to create String object:By string literalBy new keyword1) String Literal
Java String literal is created by using double quotes. For Example:
String;
Each time you create a string literal, the JVM checks the string constant pool first. If the string already exists in the pool, a reference to the pooled instance is returned. If string doesn't exist in the pool, a new string instance is created and placed in the pool. For example:
String s1="Welcome"; String s2="Welcome";//will not create new instance 
In the above example only one object will be created. Firstly JVM will not find any string object with the value "Welcome" in string constant pool, so it will create a new object. After that it will find the string with the value "Welcome" in the pool, it will not create new object but will return the reference to the same instance.
Note: String objects are stored in a special memory area known as string constant pool.Why java uses concept of string literal?
To make Java more memory efficient (because no new objects are created if it exists already in string constant pool).
2) By new keywordString s=new String("Welcome");//creates two objects and one reference variable
In such case, JVM will create a new string object in normal(non pool) heap memory and the literal "Welcome" will be placed in the string constant pool. The variable s will refer to the object in heap(non pool).
Java String Examplepublic class StringExample{ public static void main(String args[]){ String s1="java";//creating string by java string literal char ch[]={'s','t','r','i','n','g','s'}; String s2=new String(ch);//converting char array to string String s3=new String("example");//creating java string by new keyword System.out.println(s1); System.out.println(s2); System.out.println(s3); }} java strings example Java String class methods
The java.lang.String class provides many useful methods to perform operations on sequence of char values.
No.MethodDescription1
returns char value for the particular index2
returns string length3
returns formatted string4
returns formatted string with given locale5
returns substring for given begin index6
returns substring for given begin index and end index7
returns true or false after matching the sequence of char value8
returns a joined string9
returns a joined string10
checks the equality of string with object11
checks if string is empty12
concatinates specified string13
replaces all occurrences of specified char value14
replaces all occurrences of specified CharSequence15
compares another string. It doesn't check case.16
returns splitted string matching regex17
returns splitted string matching regex and limit18
returns interned string19
returns specified char value index20
returns specified char value index starting with given index21
returns specified substring index22
returns specified substring index starting with given index23
returns string in lowercase.24
returns string in lowercase using specified locale.25
returns string in uppercase.26
returns string in uppercase using specified locale.27
removes beginning and ending spaces of this string.28
converts given type into string. It is overloaded.Do You Know ? Why String objects are immutable?How to create an immutable class?What is string constant pool?What code is written by the compiler if you concat any string by + (string concatenation operator)?What is the difference between StringBuffer and StringBuilder class?What we will learn in String Handling ? Concept of StringImmutable StringString ComparisonString ConcatenationConcept of SubstringString class methods and its usageStringBuffer classStringBuilder classCreating Immutable classtoString() method

